Conditions and Treatments
Florence Neurosurgery & Spine at McLeod Health provides comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of brain, spine and peripheral nerve disorders.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Procedures performed to address abnormalities of the spine.
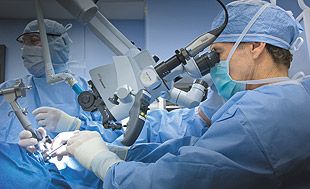
Microscopic Surgery
Surgical approach that utilizes microscopes and microsurgical instruments to assist surgeons in visualizing and repairing small structures, such as blood vessels and nerves, or for identification and removal of abnormal tissue, such as a tumor.
Lumbar Fusion
A procedure that joins two lumbar vertebrae together to immobilize the joint and reduce discomfort.
Lumbar Discectomy
A procedure where herniated disc tissue is removed from between two lumbar vertebrae to reduce pressure on the nerve root, reducing back and leg pain and improving mobility.
Lumbar Laminectomy
A procedure where the backside of the lumbar vertebrae of the lower back, called the lamina, is removed to relieve pressure in the spinal canal, often caused by bony growths.
Cervical Laminectomy/Discectomy
A procedure where the backside of the cervical vertebrae of the neck, called the lamina, is removed to relieve pressure in the spinal canal, often caused by bony growths.
Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty
A procedure in which compression fractures in the spine are reinforced through the injection of a specialized bone cement. The cement seals the tiny cracks, helping to preserve the vertebrae.
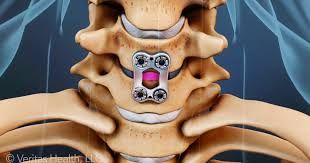
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) is a surgical procedure to treat nerve root or spinal cord compression by decompressing the spinal cord and nerve roots of the cervical spine with a discectomy in order to stabilize the corresponding vertebrae.
Complex Spinal Surgery and Instrumentation
Procedures performed to address major abnormalities of the spine.
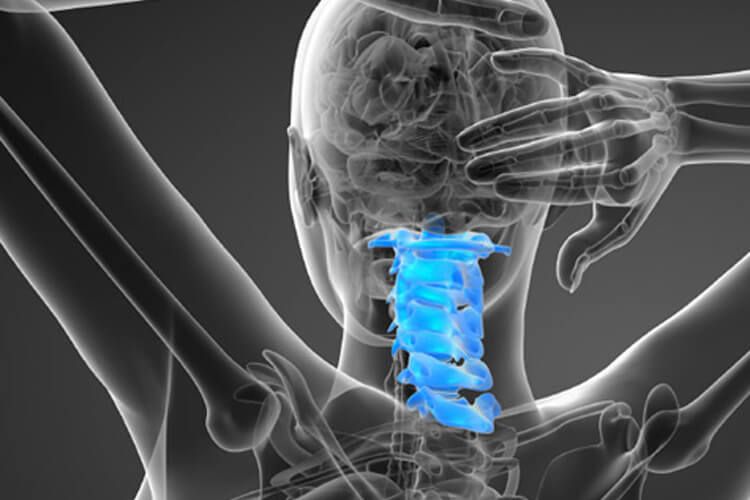
Cervical Fusion
A procedure that joins two cervical vertebrae of the neck together to immobilize the joint and reduce discomfort.
Anterior Thoracic and Lumbar Fusion
A procedure that joins two thoracic or lumbar vertebrae of the mid or lower back together from the front surface of the spine to immobilize the joint and reduce discomfort.
Direct Lateral Fusion
A minimally invasive procedure for joining spinal vertebrae by accessing the spine through a patient’s side. The surgeon carefully spreads psoas muscle fibers to access the vertebrae rather than cutting the muscle, which promotes quicker recovery time due to minimal trauma.
Cervical Artificial Disc Surgery
A procedure in which a damaged cervical disc of the neck, which provides cushioning between vertebrae, is replaced with an artificial disc to reduce pain and discomfort.
Brain Tumor Surgery
Surgical approaches for identifying and removing tumors of the brain.
Skull Base Surgery
A procedure in which surgeons access abnormalities such as tumors beneath the brain by going through the base of the skull. This approach requires less trauma to the brain, promoting quicker recovery times.
Stereotactic Craniotomy
A procedure that uses imaging technology such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) paired with the removal of a segment of the skull to access the brain.
Stereotactic Biopsy
A procedure that uses imaging technology such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computerized tomography (CT) to guide a probe into the brain to collect a tissue sample and evaluate for pathology.
Transsphenoidal Surgery
A procedure in which the front, lower area of the brain is accessed by entering through the nose and sphenoid bone located at the back of the sphenoidal sinus cavity.
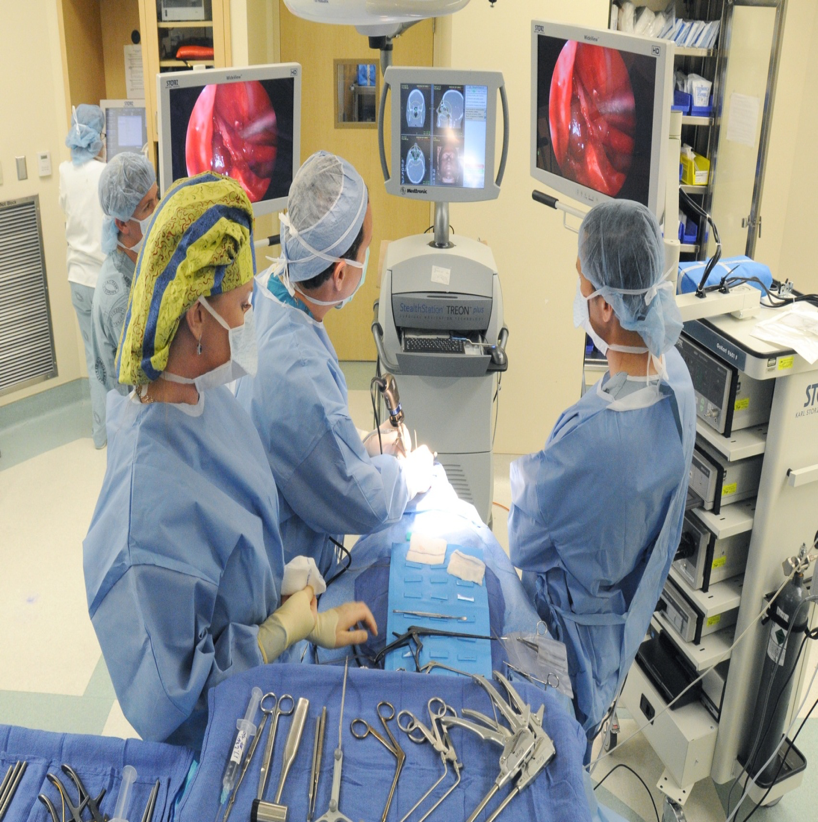
Endoscopic Surgery
A procedure which uses a small camera inserted through an opening or surgical incision so surgeons can visualize internal structures and perform invasive surgery with minimal trauma, allowing for faster recovery time.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other conditions in the brain, spine and other parts of the body. It is not surgery in the traditional sense because there's no incision. Instead, SRS uses 3-D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
Neurovascular Surgery
Procedures performed to address abnormalities of the blood vessels that supply your brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerve tissue.
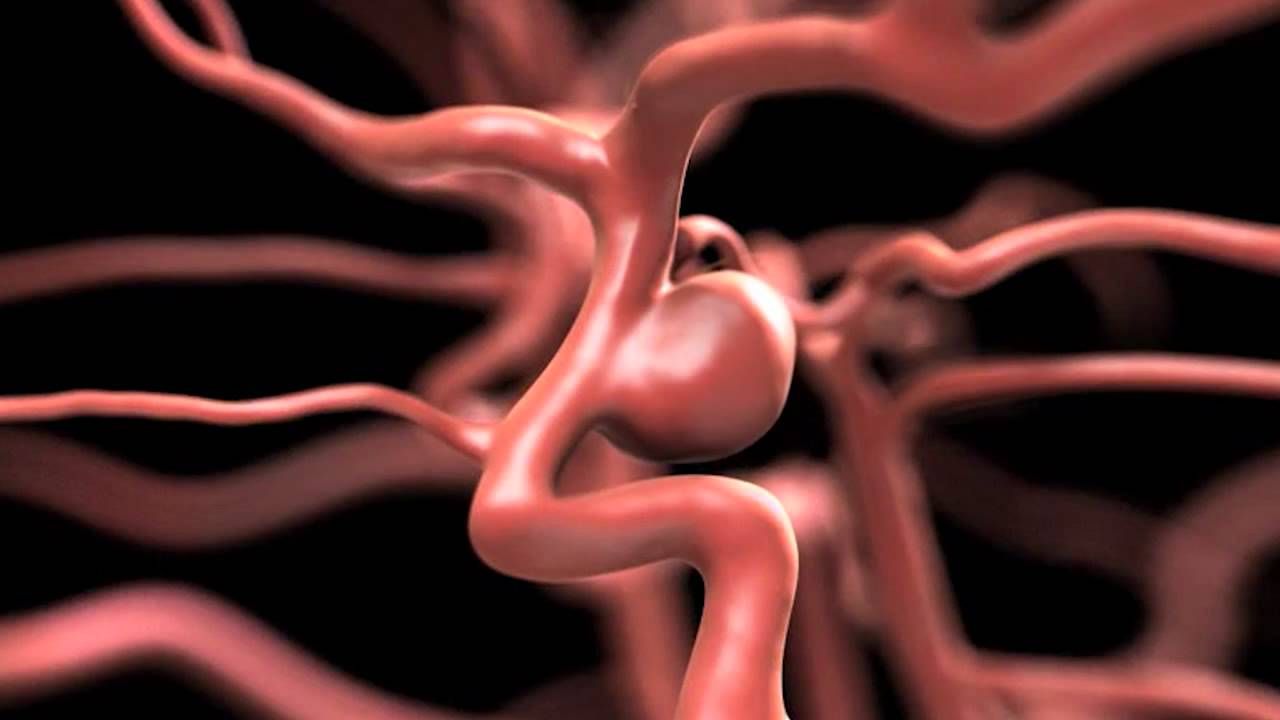
Cerebral Aneurysm Surgery
A procedure in which the surgeon repairs blood vessels within the brain that have weakened and are in danger of bursting, preventing a stroke.
Arteriovenous Malformation Surgery
A procedure that surgically removes abnormal connections between arteries and veins in the brain to prevent potential bleeding.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses many precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors and other conditions in the brain, spine and other parts of the body. It is not surgery in the traditional sense because there's no incision. Instead, SRS uses 3-D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
Microvascular Decompression
Microvascular decompression (MVD) is a neurosurgical procedure used to treat trigeminal neuralgia, a pain syndrome characterized by severe episodes of intense facial pain, and hemifacial spasm.
Peripheral Nerve and Functional Surgery
Procedures performed to address abnormalities of nerve tissue outside of the brain and spinal cord.
Carpal Tunnel Surgery
A procedure in which the transverse carpal ligament located in the wrist is cut to alleviate pressure on the median nerve, reducing carpal tunnel pain and discomfort.
Ulnar Nerve Surgery
A procedure in which the surgeon exposes and examines the ulnar nerve located in the elbow, and removes any materials that may be putting pressure on the nerve, reducing “funny bone” sensations, such as numbness, tingling, and discomfort in the arms and hands.
Vagal Nerve Stimulators
A device that is surgically placed beneath the skin of the chest that delivers electrical stimulation to the vagus nerve, a cranial nerve that runs from the brainstem through the neck, chest, and abdomen. Vagal nerve stimulators help to treat epilepsy.
Hydrocephalus Surgery
The surgical procedure to implant a VP (ventricular peritoneal) shunt.
Baclofen Pumps
The procedure for insertion of an intrathecal baclofen pump. The pump is usually placed in the abdominal wall underneath the skin while the patient is under a general anesthetic. A small catheter is inserted through a needle into the spinal fluid and is threaded upward toward the neck.
Spinal Cord Stimulators
A spinal cord stimulator (SCS) device is surgically placed under your skin and sends a mild electric current to your spinal cord. A small wire carries the current from a pulse generator to the nerve fibers of the spinal cord.
Concussion and Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury that results in a temporary loss of normal brain function. A concussion can occur following a blow to the head, neck or body that leads to a sudden shaking or jarring of the head. Many times there are no external signs of head trauma. A concussion does not always involve a loss of consciousness. The Neurosurgeons and Concussion Specialists at Florence Neurosurgery & Spine at McLeod Health offer a multidisciplinary approach to concussion recovery including a return to cognitive and physical activities, management of post concussion syndrome, and on-site vestibular rehab.
CONCUSSION SYMPTOMS